Biomass Energy: An Overview
- Biomass energy, derived from organic materials such as wood, agricultural residues, and waste, has been a part of human energy use for centuries. It represents one of the most versatile and widely used renewable energy sources, offering a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels. Biomass is considered carbon-neutral because the carbon dioxide released during its combustion is balanced by the carbon dioxide absorbed by plants during their growth
-
How Biomass Energy is Produced
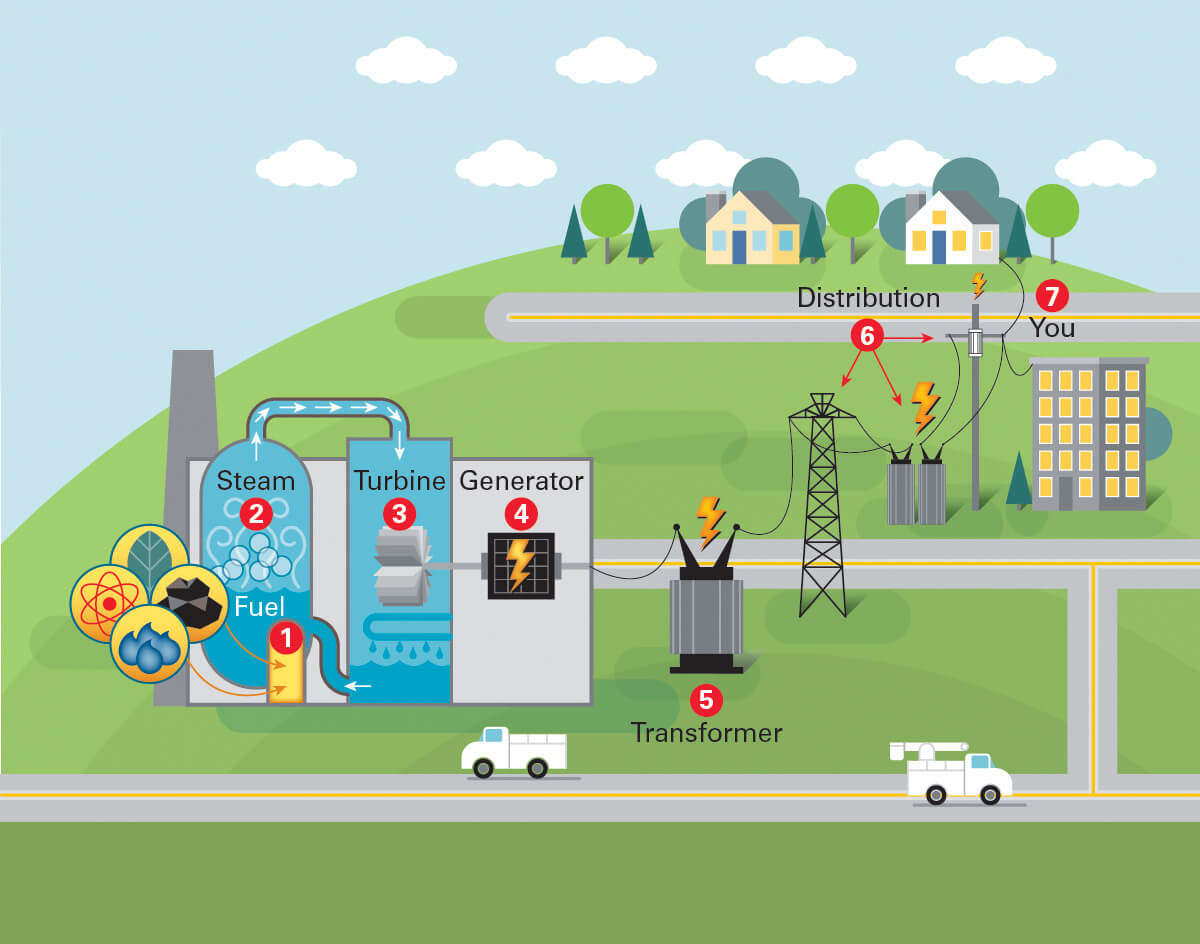
The process of producing biomass energy involves several steps, from collection to conversion into usable energy. Here’s a detailed look at the journey from raw biomass to energy production:
- Collection and Preparation of Biomass
Raw materials used in biomass energy production include agricultural residues (such as corn stalks, wheat straw), forestry by-products (like sawdust and wood chips), and organic waste from households and industries. The first step in the process is to gather these materials, followed by cleaning and sorting to remove impurities. Depending on the type of biomass, these materials may also undergo pre-treatment to improve their energy efficiency. -
Biomass can be converted into usable energy through various processes. The most common methods include:
Combustion
This is the most straightforward method, where biomass is burned in a controlled environment to produce heat. This heat generates steam, which drives turbines connected to generators to produce electricity. Biomass combustion can be done in dedicated power plants or even in boilers for residential heating.
Gasification
In this process, biomass is heated in a low-oxygen environment to produce a gas mixture known as syngas. Syngas primarily contains carbon monoxide, hydrogen, and methane, which can be used to generate electricity, fuel engines, or produce chemicals.
Anaerobic Digestion
Organic waste materials, such as food scraps, manure, and sewage sludge, are broken down by microorganisms in the absence of oxygen. This results in the production of biogas, primarily composed of methane, which can be burned to generate electricity or heat.
Pyrolysis
This method involves heating biomass in the absence of oxygen at high temperatures. The process results in the production of bio-oil, syngas, and biochar. Bio-oil can be further refined into transportation fuels, while biochar is used as a soil amendment
- Collection and Preparation of Biomass
Energy Extraction and Utilization
Once biomass has been converted into energy, the resulting output can take various forms. It may be used to generate electricity, heat homes, or provide biofuels for transportation. Biomass can also be stored for later use or distributed via power grids. The versatility of biomass allows it to be used in different sectors, including residential, industrial, and transportation, thus supporting a sustainable energy mix.
Sustainability Measures in Production
While biomass is considered a renewable resource, the sustainability of biomass production depends on factors such as sourcing and land use. In modern biomass facilities, there is a strong focus on sustainable practices. Many plants now incorporate carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies to offset emissions. Additionally, the sourcing of biomass materials is managed to avoid deforestation and ensure that energy production doesn’t come at the expense of ecological balance
Application of Biomass Energy
Biomass energy has various applications across different sectors. In the residential sector, it is commonly used in the form of heating systems that burn wood pellets or chips. Many homes use biomass boilers or stoves to provide heat during colder months. In industries, biomass is often used to power boilers and produce steam for manufacturing processes. Power plants also use biomass to generate electricity on a larger scale. Additionally, transportation fuels such as bioethanol and biodiesel are derived from biomass, reducing reliance on fossil fuels for vehicles.
Key Characteristics of Biomass Energy
- Renewable Resource: Biomass is continuously replenished through agriculture, forestry, and waste management.
- Carbon Neutrality Potential: The CO₂ emitted during biomass combustion is offset by the CO₂ absorbed by plants during their growth.
- Diverse Feedstocks: Biomass can be sourced from wood, crop residues, municipal waste, and other organic materials.
Conclusion
Biomass energy plays a crucial role in the transition to a cleaner, more sustainable energy future. By harnessing the power of organic materials, biomass helps reduce waste and can be produced locally, providing both economic and environmental benefits. Through continued innovation in production methods and sustainable practices, biomass energy can significantly contribute to reducing the global carbon footprint.
